Collection agent (2) - Cape.JS Primer
Following the previous lecture, I’ll keep rewriting the “Todo list” application by using the class CollectionAgent.
First, let’s make the function to toggle the flag “done” of the task move.
Now, the method renderTask() of the class TodoList (app/assets/javascripts/todo_list.es6) is following.
renderTask(m, task) {
m.class({ completed: task.done });
m.label(m => {
m.onclick(e => this.ds.toggleTask(task));
m.input({ type: 'checkbox', checked: task.done }).sp();
m.class({ modifying: task.modifying });
m.span(task.title);
});
(abbreviation)
}
There is checkbox in the tag <label> and if users click the checkbox,
this.ds.toggleTask(task)
the code above is run. The property ds in the class TodoList (this) doesn’t exist so rewrite this part as following.
this.agent.toggleTask(task)
Next, add the method toggleTask() to the class TaskCollectionAgent.
toggleTask(task) {
this.update(task.id, { task: { done: !task.done } });
}
The method update() defined at the parent class Cape.CollectionAgent receives 2 parameters. The first parameter is ID of “resource” and second one is the object sending to API server.
If the value of task.id is 123, the method toggleTask() sends the request to URL /api/tasks/123 by PATCH method. The object assigned to the second parameter is changed to string in Jason style and sent to the server,
Let’s compare with the same name’s method of the class TaskStore.
toggleTask(task) {
$.ajax({
type: 'PATCH',
url: '/api/tasks/' + task.id,
data: { task: { done: !task.done } }
}).done(data => {
if (data === 'OK') {
task.done = !task.done;
this.propagate();
}
});
}
There are much less codes. But, these 2 methods are not same.
The method toggleTask() of TaskStore checks whether the response of API server is 'OK'. If it’s so, it reverse the true and false of the property done of the object task and calls this.propagate(). As the result, it redraws all components related to the instance this TaskStore.
On the other hand, the method toggleTask() of TaskCollectionAgent doesn’t check the response of API server. If collection agent sends the request to API server by the method POST/PATCH/PUT/DELETE, it calls the method refresh() of itself (this) automatically after receiving the response of the server. As the result, it acquires the newest data from API server and updates the property this.objects and redraws the component, “client”.
That is how to rebuilt the function to toggle the flag “done” of the task. Make sure it works well on the browser. If you check “To buy cat’s feed” from the status of the last time and check out “Go dentist”, the screen will be like following.
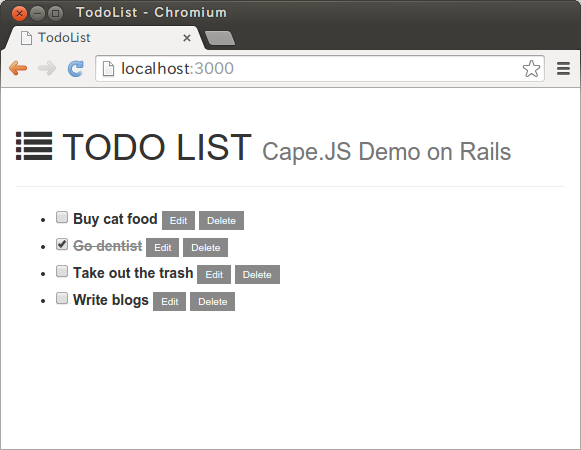
Make sure the style of the task’s title is change depending on the status of the checkbox.
Next, reintegrate the function to delete the task.
If you extract the part from the method renderTask() of the class TodoList, it’s like following.
renderTask(m, task) {
(abbreviation)
m.onclick(e => {
if (confirm('Are you sure you want to delete this task?'))
this.ds.destroyTask(task);
});
m.span('Delete', { class: 'button' });
}
Rewrite the part like following.
renderTask(m, task) {
(abbreviation)
m.onclick(e => {
if (confirm('Are you sure you want to delete this task?'))
this.agent.destroyTask(task);
});
m.span('Delete', { class: 'button' });
}
I just changed .ds to .agent.
Add the method destroyTask() the class TaskCollectionAgent.
toggleTask(task) {
this.destroy(task.id);
}
The method destroy() defined at the parent class Cape.CollectionAgent, it receives ID of “resource” as the first parameter and sends the request to API server by DELETE method.
Let’s compare the same name method of the class TaskStore.
destroyTask(task) {
$.ajax({
type: 'DELETE',
url: '/api/tasks/' + task.id
}).done(data => {
if (data === 'OK') this.refresh();
});
}
There are much less code here too.
We restored the functionality to delete task. Make sure it works well on the browser (the screen capture is omitted).
The point of this time is that the code that accesses to API server is simpler by using collection agent than the case that it uses jQuery.
On the next lecture, I’ll recreate the function to add new task and the function to change the title of existing task.